As we age, our joints face a natural challenge which are cartilage gradually wears down, ligaments lose flexibility, and bones become more fragile. For seniors, this reality impacts joint pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and reduced independence.
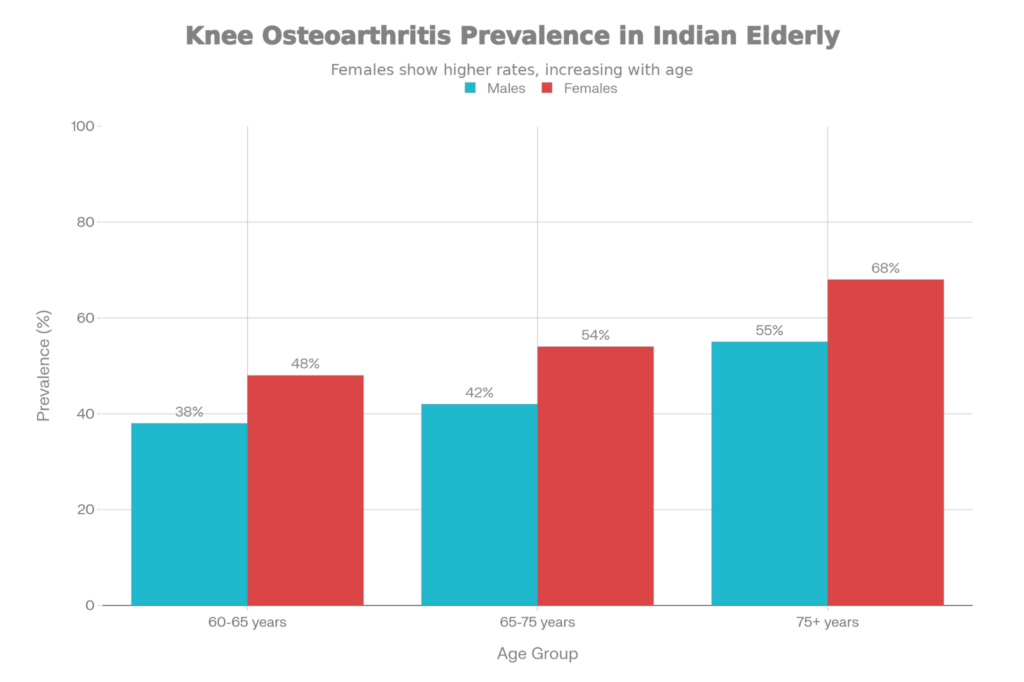
The statistics are sobering: nearly 47% of elderly persons in India aged 60 and above suffer from knee osteoarthritis alone, with prevalence reaching over 68% in women older than 75 years. Beyond the knees, age-related joint issues affect hips, shoulders, ankles, and hands. conditions collectively known as osteoarthritis that significantly impact quality of life.
However, age-related joint pain doesn’t require resignation to suffering. Modern orthopedic specialists in Indore combine decades of experience with advanced treatment strategies, helping seniors maintain mobility, independence, and active living well into their later years.
Understanding how orthopedic doctors in Indore address these challenges empowers you to seek timely care and access treatments that truly work.
Understanding Age-Related Joint Issues
What Causes Joint Deterioration in Seniors?
As we age, several factors contribute to joint decline. The protective cartilage covering bone ends gradually wears through friction and diminishes due to reduced production of cartilage-building compounds. Decreased collagen production weakens ligaments and tendons that stabilize joints. Reduced synovial fluid, the natural lubricant within joints, causes friction and pain. Additionally, hormonal changes (particularly in postmenopausal women), muscle weakness, weight gain, previous injuries, and inflammatory processes accelerate joint deterioration.
Understanding these mechanisms helps seniors appreciate why specialized joint pain treatment in Indore differs from approaches for younger patients, addressing not just symptoms but underlying age-related factors.
Most Common Age-Related Joint Problems
Knee Osteoarthritis: The most prevalent condition, affecting nearly half of Indian seniors. Gradual cartilage loss in weight-bearing knees causes pain particularly during walking, climbing stairs, and prolonged standing.
Hip Osteoarthritis: Develops in 15-20% of elderly, causing groin pain, limping, and difficulty with daily activities like putting on shoes or getting in and out of cars.
Cervical and Lumbar Spondylosis (Spine Arthritis): Progressive degeneration causing neck and back pain, sometimes radiating down arms or legs due to nerve compression.
Hand Osteoarthritis: Particularly common in elderly women, causing difficulty with fine motor tasks like buttoning, writing, and opening jars.
Shoulder Osteoarthritis: Limits overhead activities and causes pain with certain arm movements.
How Orthopedic Doctors in Indore Diagnose Age-Related Joint Issues?
Comprehensive Assessment Process
Unlike treating younger patients, orthopedic specialists in Indore recognize that elderly care requires individualized evaluation considering overall health status, medical conditions, medications, cognitive function, living situation, and realistic functional goals.
Detailed History: Understanding symptom onset, progression, activities that worsen or improve pain, impact on daily function, and how pain affects quality of life and independence.
Physical Examination: Thorough assessment of joint range of motion, stability, muscle strength, gait patterns, balance, and neurological function. Specialized orthopedic tests identify specific joint pathology.
Advanced Imaging: X-rays reveal bone structure and cartilage loss severity; ultrasound shows soft tissue inflammation and fluid accumulation; MRI provides detailed information about cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. In Indore, modern imaging facilities enable precise diagnosis.
Functional Assessment: Evaluating ability to perform activities of daily living—walking distances tolerated, stair climbing capacity, self-care ability—guides treatment toward realistic functional improvement.
Medical Optimization: Reviewing other health conditions and medications ensures orthopedic treatment integrates safely with overall health management.
Comprehensive Treatment Approach for Senior Joint Pain
Conservative Management: First-Line Treatment
Most elderly patients with age-related joint issues respond to conservative approaches, avoiding surgery when possible.
Activity Modification and Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate pain, using assistive devices when needed (canes, walkers), and balancing activity with rest periods preserve joint function while managing pain.
Physical Therapy and Exercise: Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle strength that supports joints, improving flexibility, enhancing balance and proprioception (body awareness), and preventing falls. Low-impact activities, walking, water aerobics, tai chi, gentle yoga, benefit joint health while reducing injury risk.
Heat and Cold Therapy: Heat therapy (warm baths, heating pads) relaxes stiff muscles and improves circulation; cold therapy (ice packs) reduces acute inflammation. Many elderly patients find alternating modalities most effective.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce pain and inflammation. For seniors with gastric concerns, selective COX-2 inhibitors provide safer options. Acetaminophen offers gentler pain control for those unable to tolerate NSAIDs.
Nutritional Support: Adequate vitamin D and calcium support bone health; anti-inflammatory foods (fatty fish rich in omega-3s, colorful vegetables, ginger, turmeric) may reduce joint pain; glucosamine and chondroitin supplements benefit some patients, though evidence is mixed.
Advanced Injection Therapies
When conservative measures provide insufficient relief, orthopedic specialists in Indore offer advanced injections targeting specific joint problems.
Corticosteroid Injections: Powerful anti-inflammatory medications delivered directly into affected joints provide pain relief lasting weeks to months, allowing increased activity and physiotherapy participation. Guidelines typically limit frequency to prevent adverse effects.
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: These supplements natural joint lubrication, reducing friction and improving mobility. Multiple injections provide cumulative benefit, making this option particularly effective for knee osteoarthritis.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Concentrated growth factors from the patient’s own blood promote cartilage healing and reduce inflammation—an increasingly popular option for early to moderate arthritis.
Regenerative Medicine: Advanced techniques using the body’s natural healing mechanisms address underlying cartilage damage rather than merely masking symptoms.
Surgical Options for Advanced Cases
When conservative and advanced medical treatments fail to provide adequate relief and significantly limit independence, surgery becomes appropriate.
Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive joint visualization and cleaning removes debris and inflammatory tissue, improving pain and function, particularly effective for mechanical symptoms like catching or locking.
Joint Replacement Surgery: For severe osteoarthritis unresponsive to other treatments, total joint replacement (knee, hip, shoulder) offers excellent outcomes—95%+ success rates in experienced hands. Modern implants enable excellent pain relief and functional restoration in appropriately selected elderly patients.
Specialized Care for Indore’s Elderly Population
Why Age-Related Joint Care Requires Specialization
Treating elderly patients with joint pain in Indore demands more than surgical skill. Orthopedic specialists must consider:
Medical Complexity: Many seniors have multiple health conditions (diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, kidney dysfunction) requiring careful medical optimization before and after treatment.
Medication Interactions: Managing how new treatments interact with existing medications prevents complications.
Functional Goals: Rather than pursuing maximum anatomical perfection, treatment targets realistic functional improvement, maintaining independence, reducing pain to tolerable levels, enabling preferred activities.
Rehabilitation Capacity: Elderly patients require modified rehabilitation protocols respecting reduced healing capacity while maintaining safety and preventing complications.
Fall Prevention: Special attention to balance, strength, and mobility reduces dangerous falls, a leading cause of elderly mortality and disability.
Key Treatment Principles for Age-Related Joint Issues
Early Intervention: Addressing pain promptly prevents compensatory problems and maintains activity levels
Conservative First: Most elderly patients improve with non-surgical approaches; surgery is reserved for significant functional limitation
Individualized Plans: Treatment customized to each patient’s specific joint problem, overall health, functional goals, and preferences
Multidisciplinary Approach: Coordinating orthopedic care with physiotherapy, pain management, general medicine, and mental health support
Long-Term Management: Recognizing that age-related joint disease is chronic, requiring ongoing management and periodic reassessment
Whether experiencing knee osteoarthritis, hip pain, spine problems, or other age-related joint issues, seeking evaluation from an experienced orthopedic doctor in Indore represents the crucial first step. Specialized care addressing your specific joint problem, overall health status, and personal functional goals offers realistic hope for meaningful improvement.
Modern joint pain treatment in Indore combined with expert orthopedic care can restore mobility, eliminate pain, and enable the active, independent senior life you deserve.
FAQs
What causes joint pain in elderly people?
Age-related joint pain stems from gradual cartilage deterioration, reduced synovial fluid lubrication, decreased collagen in ligaments, hormonal changes (especially postmenopause), muscle weakness, and previous injuries. Nearly 47% of Indian seniors over 60 have knee osteoarthritis alone. These natural aging processes progress gradually, with pain typically increasing after age 60 as cartilage damage accumulates. Early orthopedic evaluation helps manage symptoms before advanced degeneration occurs.
How can orthopedic specialists in Indore help manage age-related joint issues?
Orthopedic specialists in Indore diagnose specific joint problems through examination and imaging, then recommend individualized treatment—from activity modification and physiotherapy to advanced injections (corticosteroid, hyaluronic acid, PRP therapy) to surgical options when necessary. Most elderly patients improve with conservative approaches. Specialists consider overall health, medications, and functional goals, ensuring safe, effective treatment appropriate for seniors.
What is the success rate of joint treatment in elderly patients?
Conservative treatment (physiotherapy, injections, medications) succeeds in 70-80% of elderly patients, enabling pain reduction and improved mobility without surgery. When surgery becomes necessary, joint replacement achieves 95%+ success rates with high patient satisfaction even in elderly populations. Success depends on appropriate treatment selection, patient compliance with rehabilitation, and realistic functional goals.
Are elderly patients safe candidates for joint replacement surgery?
Yes, elderly patients can safely undergo joint replacement surgery when appropriately selected. Modern techniques, anesthesia advances, and comprehensive medical optimization enable excellent outcomes even in octogenarians. Safety depends on overall health status, specific joint problem severity, motivation for rehabilitation, and realistic functional expectations. An experienced orthopedic specialist in Indore assesses individual suitability.
What preventive measures help manage age-related joint health?
Key preventive strategies include: maintaining healthy weight to reduce joint stress, staying active with low-impact exercise (walking, swimming, tai chi), maintaining adequate calcium and vitamin D for bone health, anti-inflammatory nutrition, strengthening surrounding muscles through physiotherapy, managing associated conditions like diabetes, avoiding smoking, and seeking early evaluation for persistent joint pain. Preventive care delays progression and maintains senior independence.
When should elderly patients see an orthopedic doctor for joint pain?
Consult an orthopedic doctor in Indore for joint pain lasting beyond 2 weeks, affecting daily activities or sleep, accompanied by significant swelling, or limiting independence. Early evaluation prevents progressive degeneration. Don’t accept persistent pain as inevitable, specialized treatment enables continued active living. Seniors with multiple joint problems or complex medical conditions benefit particularly from comprehensive orthopedic evaluation.
Posted by : Dr. Tarkit Modi
MBBS, MS (Orthopaedics) , FIJR, FIAS- (Fortis Hospital,Delhi)
Specialist in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Shoulder, Hip, Knee & Orthopedic Surgeon in Indore

