Joint and muscle pain are among the most common health complaints in India, affecting people of all ages and activity levels. Recent studies suggest that over 40% of Indian adults experience joint or muscle pain at least once a year, with conditions ranging from mild strains to chronic arthritis. Whether it’s knee pain from sports, a stiff shoulder after long computer work, or persistent back aches as you age, knowing which healthcare professional to consult is critical for effective recovery and long-term well-being.
Dr. Tarkit Modi, a leading orthopedic surgeon in Indore with extensive experience in joint and muscle pain management, offers this guide for patients and caregivers seeking expert advice on choosing the right specialist for their orthopedic needs.
Common Causes of Joint and Muscle Pain
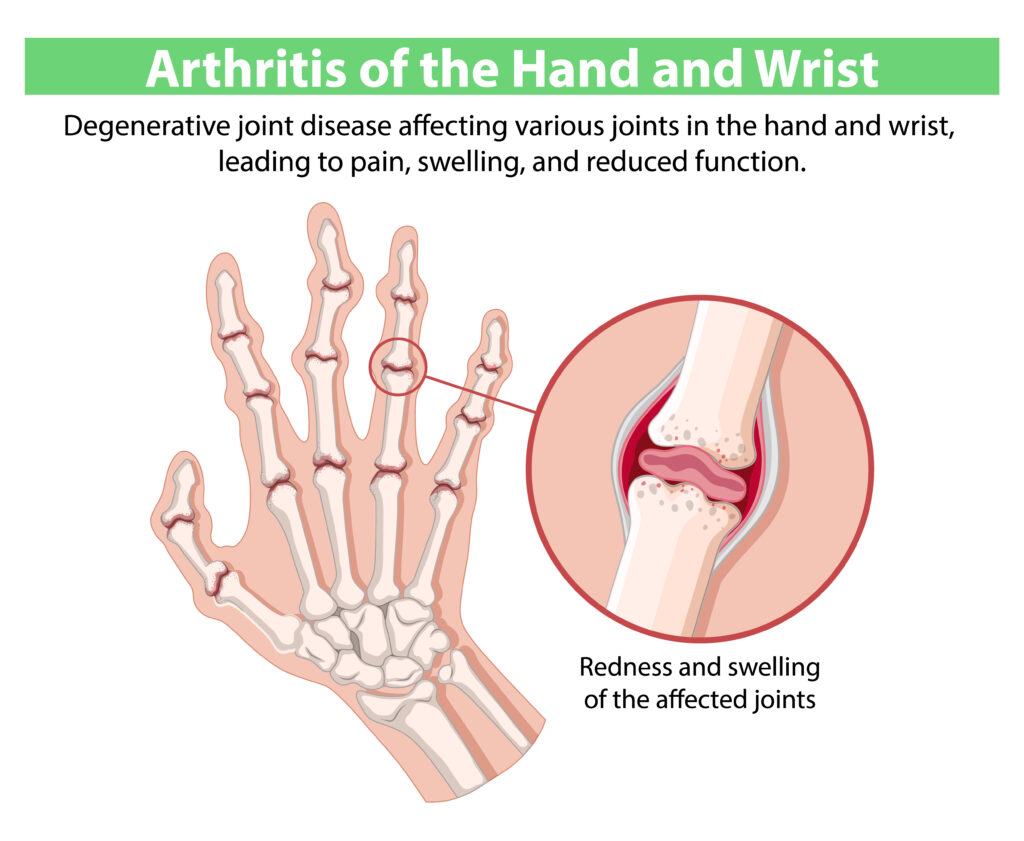
Arthritis and Inflammatory Conditions
Arthritis is a major contributor to joint pain, with osteoarthritis affecting nearly 22% of Indian adults over 40, and rheumatoid arthritis posing chronic inflammation risks for younger and middle-aged adults. These conditions result in swelling, stiffness, and pain—often requiring specialist intervention for diagnosis and ongoing management.
Sports Injuries and Accidents
Active lifestyles, including regular exercise and sports, can lead to injuries like ligament tears, sprains, dislocations, and fractures. Sudden impacts or repetitive movements may damage joints, muscles, and supporting tissues. Sports injuries are a leading cause of orthopedic consultations among younger adults.

Overuse and Muscle Strain
Prolonged or repetitive activities—such as typing, gardening, or lifting—can cause muscle strains or tendon inflammation. Many people experience mild to moderate muscle pain due to daily routines and work demands. Statistics show that 30% of musculoskeletal pain cases in urban areas are linked to overuse or occupational strain.
Age-Related Degeneration
As people age, natural wear and tear of joints and muscles leads to degeneration, decreased strength, and increased risk of pain or mobility issues. Knee osteoarthritis is increasingly recognized as a top cause of physical disability in adults over 60 years. Early intervention can help slow progression and enhance quality of life.
Types of Doctors for Joint and Muscle Pain
Orthopedic Surgeons
Orthopedic surgeons are medical experts trained to diagnose, treat, and surgically manage joint and muscle problems. They handle fractures, complex injuries, advanced arthritis, and structural abnormalities requiring interventions such as joint replacement, arthroscopy, or reconstructive procedures.
When to Consult an Orthopedic Surgeon?
See an orthopedic surgeon if:
- You have severe, persistent, or worsening joint pain
- You experience swelling, deformity, or lost mobility
- There is a suspected fracture or dislocation
- Non-surgical treatments have failed
India performs over 250,000 joint replacement surgeries annually, underscoring the expertise and role of orthopedic surgeons for advanced conditions.
Physiotherapists
Physiotherapists are trained in rehabilitation, exercise therapy, pain relief, and functional restoration techniques. They work closely with orthopedic specialists to guide recovery after injury or surgery and manage milder cases of muscle pain, stiffness, or postural problems.
Role in Rehabilitation and Recovery
Consult a physiotherapist for:
- Rehabilitation after orthopedic surgeries
- Chronic pain from muscle strains and overuse
- Exercise programs to improve strength and mobility
- Preventive strategies for sports injuries
Rheumatologists
Rheumatologists focus on autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and ankylosing spondylitis. They diagnose and treat conditions when joint pain arises from underlying immunological problems.
For Autoimmune and Chronic Conditions
See a rheumatologist if:
- You have chronic joint swelling not responding to routine care
- Lab tests reveal autoimmune markers
- Joint pain is accompanied by systemic symptoms like fatigue or fever
General Practitioners
General practitioners (GPs) are often the first point of contact for new or mild joint/muscle pain. They provide initial assessments, manage simple strains, and refer to specialists if more advanced care is needed.
Initial Assessment and Referrals
A GP is appropriate for:
- Mild, short-term aches and pains
- Basic medication management
- Referrals to orthopedic surgeons, physiotherapists, or rheumatologists as needed
Comparison Table: Specialists for Joint and Muscle Pain
| Specialist Type | Main Focus | Conditions Treated | Typical Role | Recovery Support |
| Orthopedic Surgeon | Surgery, structural care | Fractures, arthritis, injuries | Diagnosis, surgery, | Pre/post-op guidance, |
| procedures | long-term management | |||
| Physiotherapist | Rehab, exercise therapy | Strains, overuse, post-op | Recovery programs | Personalized rehab plans |
| Rheumatologist | Autoimmune care | RA, lupus, spondylitis | Diagnosis, medication | Systemic monitoring |
| General Practitioner | Primary assessment | Mild pain, initial trauma | Referral, basic care | Early pain management |
Choosing the right specialist for joint or muscle pain is the first step toward lasting relief and a better quality of life. By understanding your symptoms and seeking care from the most qualified expert, whether it’s an orthopedic surgeon, physiotherapist, rheumatologist, or general practitioner, you improve your chances for a faster and more effective recovery.
If you’re struggling with joint or muscle pain, don’t wait for your condition to worsen. Book a consultation with Dr. Tarkit Modi, a trusted orthopedic surgeon in Indore, to receive a clear diagnosis and personalized treatment for lasting pain relief and mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who is the best doctor to consult for joint pain?
For persistent or severe joint pain, an orthopedic surgeon is ideal, especially for diagnosis and advanced treatments. For chronic inflammatory joint pain, a rheumatologist may be best.
When should I see an orthopedic surgeon vs a physiotherapist?
Consult an orthopedic surgeon for fractures, deformity, or failed conservative care. A physiotherapist helps with mild strains, post-surgical rehab, and exercise-based pain management.
Can muscle pain be treated without surgery?
Yes, most muscle strains respond well to physiotherapy, rest, and pain relief measures. Surgery is rare unless injury is severe or chronic.
How to choose the right specialist for chronic joint pain?
Consider the cause (injury, arthritis, autoimmune), look for experienced experts, check reviews, and ensure ongoing support and rehabilitation options.
Are there preventive measures for joint and muscle pain?
Regular exercise, posture awareness, healthy weight, and ergonomic modifications help prevent pain and reduce risk of injury.
How long does recovery take after consulting a joint pain specialist?
Recovery for mild issues may be 1–2 weeks; post-surgical rehab lasts 3–6 months; chronic conditions may require longer-term management and follow-up.
What treatments are available for sports-related joint injuries?
Treatments range from rest, ice, physiotherapy exercises, and anti-inflammatory medications to arthroscopy, ligament repair, or joint replacement for severe cases.
Can general practitioners manage mild joint or muscle pain?
GPs handle simple strains and short-term aches effectively; complex or chronic pain often needs referral to an orthopedic specialist or physiotherapist.
Posted by : Dr. Tarkit Modi
MBBS, MS (Orthopaedics) , FIJR, FIAS- (Fortis Hospital,Delhi)
Specialist in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Shoulder, Hip, Knee & Orthopedic Surgeon in Indore