Understanding bone fractures is crucial for anyone seeking orthopedic care, as over 4.4 million people experience traumatic fractures annually in countries like India. As Dr. Tarkit Modi, an experienced orthopedic surgeon in Indore with years of specialized expertise in orthopedic care. I frequently encounter patients who need clear information about different fracture types to make informed treatment decisions.
Fractures are breaks or cracks in bones that occur when the bone cannot withstand applied force. In India, fracture incidence varies significantly by region, with hip fractures alone affecting 129 per 100,000 people over age 50, and women being 1.5 times more likely to experience fractures than men. Understanding the seven main types of fractures helps patients recognize the severity of their injury and the appropriate treatment approach.
Understanding Bone Fractures: Medical Classification
Fractures are medically classified based on several factors, including the direction of the break, the extent of bone damage, and whether the skin is involved. Clinical studies show that 43.83% of fractures occur in the 18-50 age group, while 41.33% affect individuals over 50. The most common causes include vehicular accidents (47.07%) and falls from height (21.03%).
The proper classification of fractures is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach. Research indicates that 81.07% of fracture cases require operative management, while 18.93% can be treated conservatively, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and classification.
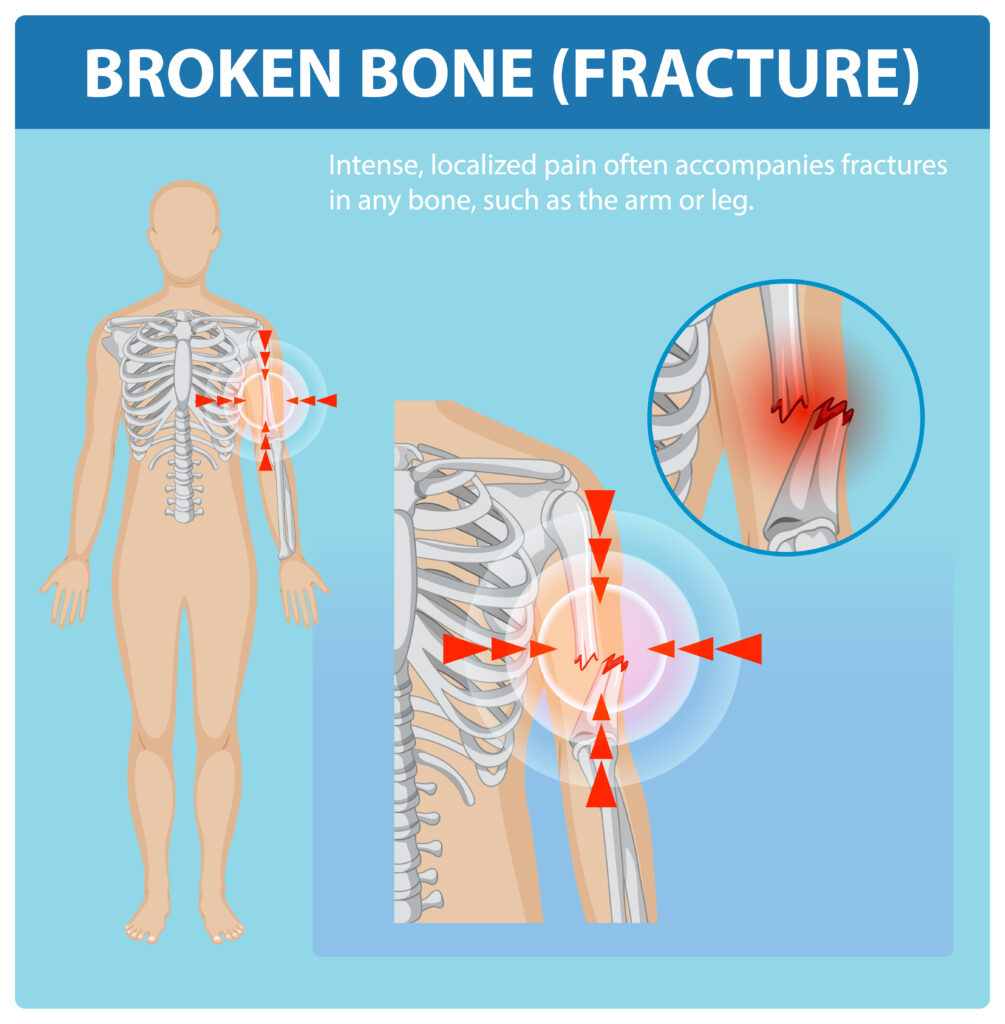
Types of Bone Fractures Explained
1. Simple (Closed) Fractures
Simple fractures occur when the bone breaks but the surrounding soft tissue remains intact with no open wounds. These fractures may still cause significant soft tissue damage and can affect nearby nerves, arteries, or tendons. The healing timeline for simple fractures typically ranges from 6-8 weeks for most bones, with fingers and toes healing fastest at 3-6 weeks.
Simple fractures are generally easier to treat and have lower complication rates since there’s no risk of external contamination. However, proper immobilization and monitoring remain crucial for optimal healing.
2. Open (Compound) Fractures
Open fractures involve a skin wound that connects to the fracture site. These fractures carry significant infection risk, with complication rates varying based on the Gustilo-Anderson classification system. Type I open fractures (wounds ≤1 cm) have the best prognosis, while Type IIIC fractures involving vascular injury require immediate surgical intervention.
In my practice treating trauma cases in Indore, I emphasize that any fracture with a skin wound should be assumed to be an open fracture to limit infection risk. These injuries require immediate surgical debridement and often multiple procedures for optimal outcomes.
3. Transverse Fractures
Transverse fractures create a straight, horizontal break completely across the bone. These typically result from direct blows and can cause the bone ends to become displaced and pulled apart by muscle forces. The clean break pattern often allows for good healing outcomes when properly aligned and stabilized.
Treatment usually involves reduction to realign the bone fragments followed by immobilization through casting or surgical fixation, depending on the degree of displacement.
4. Oblique and Spiral Fractures
Oblique fractures occur at an angle across the bone, while spiral fractures twist diagonally, resembling a corkscrew. Spiral fractures most commonly affect long bones such as the femur and tibia, typically resulting from twisting forces during sports activities.
These fracture patterns can be unstable due to their geometry, often requiring surgical fixation with plates, screws, or intramedullary nails to maintain proper alignment during healing.
5. Comminuted Fractures
Comminuted fractures occur when the bone shatters into three or more pieces. These fractures typically result from high-energy trauma and are associated with significant soft tissue damage and swelling. The multiple bone fragments receive inadequate blood supply, making them slower to heal and sometimes requiring additional surgical procedures.
Studies show that comminuted fractures have longer healing times, often extending beyond the typical 6-8 week timeframe, and may require 10-16 weeks or more for complete recovery.
6. Greenstick (Incomplete) Fractures
Greenstick fractures are incomplete breaks where the bone cracks partway across, similar to how a green stick bends but doesn’t completely break. These fractures predominantly occur in children whose bones are more pliable and flexible than adult bones.
Pediatric fracture studies show that children’s bones heal approximately 1.5-2 times faster than adult bones, with greenstick fractures typically healing within 3-4 weeks. The flexibility of children’s bones allows for this unique fracture pattern that’s rarely seen in adults.
7. Impacted Fractures
Impacted fractures occur when one bone fragment is driven into another, making the fracture line indistinct and assessment difficult. These commonly occur in elderly patients after falls, such as the classic Colles’ fracture of the wrist from falling on an outstretched hand.
Clinical data show that impacted fractures often have good stability due to the compaction of bone fragments, but may require careful monitoring to ensure proper alignment is maintained during healing.
Treatment Options for Different Fractures
Conservative Management
Research indicates that approximately 19% of fractures can be successfully treated with non-surgical methods including casting, splinting, and immobilization. Conservative treatment is typically appropriate for:
- Stable, well-aligned fractures
- Incomplete fractures in children
- Fractures in non-weight-bearing bones
- Patients with high surgical risks
Surgical Intervention
Modern orthopedic practice shows that 81% of fractures benefit from surgical treatment, which may include internal fixation with plates and screws, intramedullary nailing, or external fixation. Surgical intervention is typically recommended for:
- Displaced fractures requiring reduction
- Open fractures needing debridement
- Fractures affecting joint surfaces
- Cases where conservative treatment has failed
Advanced Treatment Technologies
In my practice in Indore, I utilize advanced technologies, including computer-assisted surgery, minimally invasive techniques, and robotic-assisted procedures for complex fracture reconstruction. These technologies allow for:
- More precise fracture reduction
- Smaller incisions and less tissue damage
- Faster recovery times
- Reduced complications
Fracture Healing Timeline and Recovery
The fracture healing process follows predictable stages: inflammatory (first few days), reparative (1-6 weeks), and remodeling (6 weeks to several months). Understanding these stages helps patients set realistic expectations for recovery.
Clinical studies demonstrate that factors affecting healing include patient age, nutrition, smoking status, and the presence of medical conditions like diabetes. Younger patients typically heal 1.5-2 times faster than older adults, with pediatric fractures often healing within 3-6 weeks compared to 6-12 weeks in adults.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention?
As an orthopedic specialist in Indore, I advise patients to seek immediate medical care for:
- Obvious bone deformity or displacement
- Open wounds near fracture sites
- Numbness or inability to move the affected area
- Severe pain that doesn’t improve with basic measures
- Signs of infection (fever, increased swelling, redness)
Studies show that delayed treatment beyond 24 hours can increase complication rates and mortality, particularly in elderly patients with hip fractures. Early intervention is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Understanding the seven types of fractures empowers patients to make informed decisions about their orthopedic care. Each fracture type requires specific treatment approaches, and proper classification is essential for optimal outcomes. With modern treatment techniques, most fractures heal successfully, with overall complication rates ranging from 2.6-10% depending on fracture type and patient factors.
If you suspect a fracture, don’t delay seeking professional medical evaluation. Contact Dr. Tarkit Modi’s clinic in Indore at +91-8959000069 for expert orthopedic consultation and advanced fracture treatment using the latest surgical techniques and technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which fracture takes the longest to heal?
Femur fractures typically take the longest to heal, requiring 10-16 weeks for complete recovery. Comminuted fractures and those with poor blood supply, such as scaphoid fractures in the wrist, also have extended healing times. Factors like patient age, nutrition, and smoking status significantly impact healing duration.
What are the most painful types of fractures?
The most painful fractures include femur breaks, spinal vertebrae fractures, and open (compound) fractures. Orthopedic surgery is considered among the most painful medical procedures, with fracture pain being particularly severe due to mechanical distortion of nerve fibers in bone tissue.
How long does it take for different fractures to heal?
Healing times vary by location: fingers and toes heal in 3-6 weeks, wrists in 6-8 weeks, ankles in 6-10 weeks, and legs in 10-16 weeks. Pediatric fractures heal 1.5-2 times faster than adult fractures due to better blood supply and bone remodeling capacity.
What is the difference between open and closed fractures?
Closed fractures have intact skin with no external wounds, while open fractures involve skin breaks that connect to the fracture site. Open fractures carry significant infection risk and typically require immediate surgical intervention, while closed fractures may be treated conservatively or surgically depending on displacement.
When do fractures require surgery?
Research shows that 81% of fractures require surgical intervention. Surgery is typically needed for displaced fractures, open fractures, fractures affecting joint surfaces, or when conservative treatment fails. Modern minimally invasive techniques allow many fractures to be treated surgically with smaller incisions and faster recovery.
What complications can occur with fractures?
Common complications include delayed healing, infection, nerve damage, and chronic pain affecting up to 61.7% of patients after certain fractures. Chronic fracture pain lasting more than 3 months affects a significant percentage of patients and requires specialized pain management approaches.
How can I prevent fractures?
Fracture prevention includes maintaining bone density through proper nutrition (calcium and vitamin D), regular exercise, fall prevention measures, and avoiding high-risk activities. For elderly patients, addressing osteoporosis and home safety modifications can significantly reduce fracture risk.
Should I see a specialist for my fracture?
You should consult an orthopedic specialist for displaced fractures, open wounds, persistent pain, or if conservative treatment isn’t improving your condition. Dr. Tarkit Modi’s expertise in advanced fracture treatment and joint reconstruction ensures optimal outcomes using the latest surgical techniques available in Indore.
Posted by : Dr. Tarkit Modi
MBBS, MS (Orthopaedics) , FIJR, FIAS- (Fortis Hospital,Delhi)
Specialist in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Shoulder, Hip, Knee & Orthopedic Surgeon in Indore