Knee replacement surgery has transformed millions of lives worldwide, offering renewed mobility and freedom from chronic pain. But once you’ve invested in this life-changing procedure, a natural question arises: how long will it last? The encouraging news is that modern knee implants are more durable than ever before. Research shows that approximately 82% of total knee replacements last 25 years or more. However, the longevity of your knee replacement isn’t just about the implant itself; it depends significantly on how you care for it after surgery.
Understanding the factors that influence knee replacement longevity and following evidence-based care strategies can help you maximize the lifespan of your new knee and enjoy decades of pain-free movement.
Understanding Knee Replacement Lifespan: What the Data Shows?
Modern knee replacement technology has made remarkable strides. Studies tracking thousands of patients reveal impressive survival rates: 99% of knee replacements remain functional at 5 years, 91% at 10 years, 93% at 15 years, 90% at 20 years, and 82% at 25 years. Some newer implant designs show potential to last 30 years or longer with proper care.
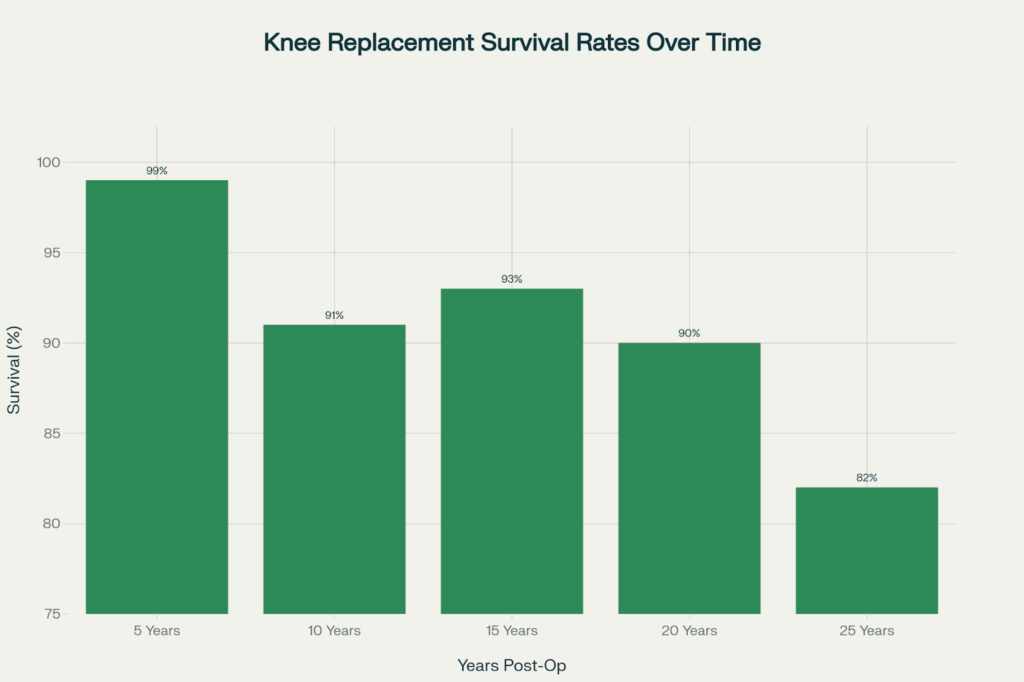
Research shows that modern knee replacements demonstrate excellent longevity, with 82% of total knee replacements lasting 25 years or more
These statistics represent averages across diverse patient populations. Your individual outcome depends on multiple factors, including age at surgery, body weight, activity choices, implant quality, and commitment to post-operative care.
Key Factors That Determine How Long Your Knee Replacement Lasts
- Age at the Time of Surgery
Patients over 70 years old achieve a 94% survival rate at 10 years, compared to just 83% for those younger than 55. This difference occurs because younger, more active patients typically place greater mechanical stress on their implants over longer periods. However, this doesn’t mean younger patients should delay necessary surgery—living with severe pain and limited mobility negatively affects overall health and quality of life.
- Body Weight Management
Your weight directly influences the stress placed on your knee implant. Every kg of excess body weight translates to approximately four kg of pressure on your knees during walking. Studies demonstrate that patients who achieve substantial weight loss after knee replacement experience a 43% lower risk of revision surgery compared to those who maintain higher body weights. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and appropriate exercise represents one of the most effective ways to make knee replacement last longer.
- Physical Activity Choices
While staying active supports joint health, the type of activity matters enormously. High-impact exercises create joint loads up to 500% of body weight, accelerating implant wear. Running generates forces approximately three times your body weight on the knee joint, while jumping creates even higher forces. Surgeons strongly recommend transitioning to low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, walking, and gentle strength training to optimize implant longevity.
- Implant Quality and Surgical Technique
Advanced implant materials and design improvements contribute significantly to extended lifespan. Modern prostheses manufactured with highly cross-linked polyethylene and refined bearing surfaces demonstrate superior wear resistance compared to older designs. Equally important is surgical precision, proper alignment and positioning during the procedure fundamentally affects long-term outcomes
- Consistent Follow-Up Care
Regular monitoring allows early detection of potential problems before they require major intervention. Following recommended follow-up schedules, typically at 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter, enables your orthopedic surgeon to identify issues like implant loosening, wear, or infection in early, more treatable stages.
Evidence-Based Tips to Increase Knee Replacement Longevity
1. Commit to Your Rehabilitation Program
Physical therapy isn’t optional, it’s essential for optimal outcomes. Dedicated rehabilitation strengthens the muscles supporting your knee joint, improves range of motion, and establishes proper movement patterns that protect your implant Most patients achieve significant improvements within 3-6 months, with continued gains up to one year post-surgery.
2. Maintain Healthy Body Weight
Achieving and sustaining a healthy weight reduces mechanical stress on your implant, significantly extending its functional life. Focus on whole foods, including lean proteins, fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. These nutrient-dense choices promote healing, reduce inflammation, and support long-term joint health.
3. Choose Low-Impact Physical Activities
Protect your investment by selecting activities that maintain fitness without excessive joint stress. Recommended exercises include:
- Swimming and water aerobics: Buoyancy eliminates impact while providing excellent cardiovascular and strength benefits
- Cycling: Stationary or outdoor cycling on smooth terrain builds leg strength with minimal joint loading
- Walking: Regular walking on level surfaces maintains mobility and cardiovascular health
- Golf: Using a cart and avoiding excessive twisting protects the knee while enjoying recreation
- Elliptical training: Provides cardio benefits without the impact of running
- Gentle yoga: Improves flexibility and balance; avoid deep squats and twisting poses
Avoid high-impact and high-risk activities including running, jumping, contact sports (football, basketball, soccer, rugby), skiing, gymnastics, and heavy weightlifting.
4. Follow a Joint-Healthy Diet
Nutrition directly impacts inflammation, bone health, and tissue repair. Optimize your diet with these knee implant care after surgery nutritional strategies:
Lean Proteins (chicken, fish, tofu, legumes): Essential for tissue repair and muscle maintenance; aim for 1 gram per kilogram of body weight
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (salmon, mackerel, sardines, flaxseeds, walnuts): Reduce inflammation and support joint health
Calcium and Vitamin D (dairy products, leafy greens, fortified plant-based milks): Critical for bone strength; spend 15-20 minutes daily in sunlight for vitamin D synthesis
Vitamin C (citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, cauliflower): Supports collagen formation in ligaments and tendons
Antioxidant-Rich Foods (berries, spinach, carrots, colorful vegetables): Combat inflammation and promote healing
Avoid: Processed foods, excessive sugar, alcohol, and high-sodium items that increase inflammation and slow healing
5. Attend Regular Follow-Up Appointments
Don’t skip routine checkups even when feeling great. Most complications develop gradually, often without symptoms in the early stages. Regular visits allow your orthopedic surgeon to monitor implant positioning, assess for wear or loosening, and identify potential problems through clinical examination and periodic X-rays before they become serious. Standard follow-up typically continues annually after the first year, though your surgeon may adjust frequency based on individual factors.
6. Protect Your Knee from Injury
Falls and trauma can damage your prosthesis or surrounding structures. Implement fall-prevention strategies, including:
- Using handrails on stairs
- Installing grab bars in bathrooms
- Removing tripping hazards like loose rugs
- Wearing supportive, non-slip footwear
- Using assistive devices as recommended
- Avoiding slippery surfaces (ice, wet grass, mud)
- Taking small steps and avoiding pivoting or twisting movements
7. Practice Proper Body Mechanics
Learn and consistently use correct movement techniques:
- Keep your knee pointing straight ahead during all activities
- Avoid crossing your legs while sitting
- Use firm chairs with armrests and back support; avoid low sofas
- Don’t place pillows directly under your knee (use under calf instead)
- Avoid prolonged sitting—move every 45-60 minutes
- When climbing stairs: “good leg up, bad leg down”
8. Manage Chronic Health Conditions
Conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoporosis can affect implant longevity. Work closely with your healthcare team to optimize management of these conditions through medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring.
9. Quit Smoking
Smoking narrows blood vessels, impairs healing, and increases infection risk. If you smoke, quitting represents one of the most impactful steps you can take to improve surgical outcomes and long-term implant survival.
10. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to changes in your knee. New or worsening pain, swelling, warmth, stiffness, instability, or clicking sounds warrant prompt evaluation. Early intervention for developing problems prevents progression and may avoid more extensive treatment later.
Maximizing Your Investment in Mobility
Your knee replacement represents both a significant medical intervention and an investment in your quality of life. While modern implants are engineered for exceptional durability, their longevity ultimately depends on the partnership between advanced surgical technique and your commitment to long-term care. By following these evidence-based strategies to increase knee replacement lifespan, you can enjoy decades of improved mobility, reduced pain, and active participation in the activities you love.
Dr. Tarkit Modi combines surgical excellence with comprehensive patient education, ensuring you have both the technical expertise and the knowledge needed for optimal long-term outcomes. Contact Dr. Tarkit Modi’s clinic today at +91-8959000069 to schedule a consultation and discover how advanced surgical techniques combined with personalized post-operative guidance can help you achieve lasting relief from knee pain and maximum implant longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does a knee replacement usually last?
Modern knee replacements typically last 15-20 years on average, with approximately 82% lasting 25 years or more. Some newer implants may last 30+ years with excellent care. Survival rates are 99% at 5 years, 91% at 10 years, and 90% at 20 years.
What are the best ways to increase knee replacement longevity?
Key strategies include maintaining healthy body weight, choosing low-impact activities over high-impact sports, following your rehabilitation program consistently, eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s and lean protein, attending regular follow-up appointments, protecting your knee from falls, and avoiding activities that twist or overload the joint.
Does exercise improve the lifespan of a knee implant?
Yes, but the type matters significantly. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, walking, and gentle strength training strengthen supporting muscles and improve joint stability, extending implant life. High-impact activities like running and jumping accelerate wear and should be avoided.
Which activities should I avoid after knee replacement surgery?
Avoid running, jumping, high-impact sports (football, basketball, soccer, skiing), contact sports, heavy weightlifting, activities with twisting motions, prolonged kneeling, and anything with high fall risk. These activities can damage the prosthesis or accelerate wear.
What diet supports long-term joint health after surgery?
Focus on lean proteins (1g per kg body weight), omega-3 fatty acids from fish and nuts, calcium and vitamin D for bone health, vitamin C for collagen formation, antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and alcohol that increase inflammation.
How often should I follow up with my doctor after knee replacement?
Standard follow-up schedule includes appointments at 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year after surgery, then annually thereafter. Your surgeon may adjust frequency based on individual factors. Regular monitoring allows early detection of potential problems.
Can modern implants last more than 20 years?
Yes. Research shows 90% of knee replacements survive 20 years, and 82% last 25 years. With advances in implant materials and surgical techniques, some newer prostheses may function well for 30 years or longer, especially when patients follow recommended care guidelines.
Posted by : Dr. Tarkit Modi
MBBS, MS (Orthopaedics) , FIJR, FIAS- (Fortis Hospital,Delhi)
Specialist in Joint Replacement and Arthroscopy, Shoulder, Hip, Knee & Orthopedic Surgeon in Indore